

Rising Film Evaporator
A Rising Film Evaporator (RFE) is a vertical heat exchanger designed to concentrate solutions by evaporating the solvent. It is particularly effective for low-viscosity liquids and is widely used in industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.
How It Works
- Liquid Feed Entry: The liquid enters the evaporator from the bottom of the tubes.
- Heat Transfer: Steam or another heating medium heats the liquid as it flows upward inside the tubes.
- Film Formation: The heat causes the liquid to boil, forming vapor. The vapor pushes the liquid upward, creating a thin film along the tube walls.
- Co-Current Flow: The vapor and liquid flow together upward, enhancing turbulence and improving heat transfer efficiency.
- Vapor-Liquid Separation: At the top, the vapor and remaining liquid are separated in a vapor-liquid separator.
Features of Rising Film Evaporators
- Continuous Process: Operates continuously, making it ideal for large-scale applications.
- High Heat Transfer Efficiency: The co-current flow and turbulence improve heat transfer rates.
- Low Residence Time: The liquid spends minimal time in the heated tubes, reducing the risk of thermal degradation.
- Scalability: Can be scaled for small or large production needs.
- Adaptability: Handles low-viscosity liquids and is suitable for heat-sensitive materials.
Unique Operating Conditions
- Vacuum Operation: Can operate under vacuum for low-temperature evaporation, protecting heat-sensitive substances.
- Multi-Effect Setup: Can be integrated into multi-effect systems for improved energy efficiency.
Common Challenges Addressed by RFEs
- Thermal Sensitivity: The short residence time minimizes heat exposure, preserving product quality.
- Foaming Liquids: Effectively handles foaming liquids by separating vapor and liquid efficiently.
- Energy Efficiency: Reduces energy consumption through optimized heat transfer.
Applications
- Food and Beverage: Concentrating juices, dairy products, and sweeteners.
- Pharmaceuticals: Solvent recovery and concentration of active ingredients.
- Chemical Industry: Evaporation of low-viscosity or heat-sensitive fluids.
- Effluent Treatment: Recovery of water and valuable components.
Key Benefits
- High Efficiency: Optimized heat transfer and reduced energy usage.
- Gentle Processing: Preserves the quality of heat-sensitive materials.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of low-viscosity liquids.
- Compact Design: Saves space while maintaining high throughput.
Material of Construction
- Options: SS 304, SS 316, MS, or as per client requirements.
Rising Film Evaporators are highly efficient and versatile systems, making them a preferred choice for
industries requiring reliable and consistent evaporation processes.
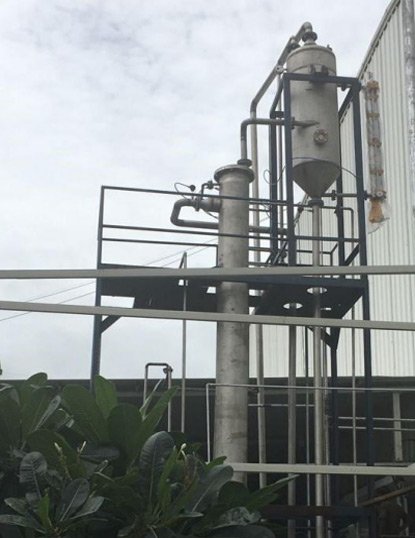

Process Flow for Rising Film Evaporator (RFE) System
Feed Solution Inlet → (Liquid enters the evaporator from the
bottom of the tubes)
Heat Transfer Section → (Steam or another heating medium indirectly heats the
liquid as it flows upward)
Film Formation → (Heat causes boiling, generating vapor that pushes the liquid
upward)
Co-Current Flow → (Vapor and liquid flow together upward, enhancing
turbulence and heat transfer)
Vapor-Liquid Separator → (At the top, vapor and remaining liquid are efficiently
separated)
Final Collection Tank → (Stores concentrated liquid for further processing)
Vapor Outlet → (Separated vapor is removed for condensation or reuse)
Key Equipment Involved
Feed Pump (Ensures controlled liquid entry into the evaporator)
Heated Tube Bundle (Provides indirect heat transfer for controlled evaporation)
Rising Film Tubes (Allow liquid to move upward while forming a thin film)
Vapor-Liquid Separator (Separates entrained liquid droplets from vapor stream)
Vacuum System (Optional: Reduces boiling point for better energy efficiency)
Condensation Unit (Recovers vapor for reuse or disposal)
Final Collection Tank (Stores concentrated solution for further use)