

Solvent Recovery Plants
Solvent Recovery is a process used to clean and reuse solvents that have been used in industrial processes. Instead of throwing away the used solvent, it is purified and recycled, saving money and reducing waste. This process is common in industries like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food production.
How Does It Work?
- Collecting Used Solvent: The waste solvent is collected from the production process.
- Heating: The solvent is heated to separate it from impurities. This works because solvents and impurities have different boiling points.
- Vaporization: The solvent turns into vapor, leaving behind the impurities.
- Condensation: The vapor is cooled down and turns back into liquid form.
- Purified Solvent: The clean solvent is collected and ready to be reused in the production process.
Why Is It Important?
- Cost Savings: Reusing solvents reduces the need to buy new ones.
- Eco-Friendly: It minimizes waste and prevents pollution.
- Efficient Production: Ensures a steady supply of clean solvents for industrial use.
Applications
- Pharmaceuticals: Recovering solvents used in making medicines.
- Food Industry: Recycling solvents used in flavour extraction.
- Chemical Industry: Reusing solvents for dyes, pigments, and other chemicals.
Benefits
- Saves money by reducing solvent purchase costs.
- Protects the environment by reducing waste.
- Improves efficiency in industrial processes.
Steps
Waste Solvent Collection → Pre-Filtration → Heating / Distillation → Vaporization → Condensation → Purified Solvent Storage → Solvent Recycling → Waste Disposal

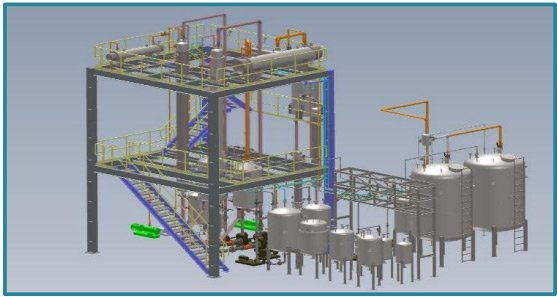
Process Flow for Solvent Recovery Plant
Waste Solvent Collection → (Used solvents are gathered from the production process)
Pre-Treatment (Optional) → (Solvent may undergo filtration or chemical
treatment to remove bulk contaminants)
Heating Process → (Solvent is heated, separating it from impurities based on boiling point differences)
Vaporization Stage → (Solvent turns into vapor, leaving behind non-volatile impurities)
Condensation System → (Vapor is cooled and converted back into liquid form)
Purified Solvent Collection → (Recovered solvent is stored and ready for reuse)
Residue Management → (Leftover impurities are safely disposed of or treated further)
Key Equipment Involved
Waste Solvent Storage Tanks (Safely collects used solvents)
Pre-Treatment Filtration System (Optional: Removes larger contaminants before distillation)
Distillation Column / Evaporator (Performs separation based on boiling points)
Condenser Unit (Cools solvent vapor for liquid recovery)
Vacuum System (Optional) (Reduces boiling point for energy-efficient operation)
Final Collection Tanks (Stores purified solvent for reuse)
Residue Handling System (Manages separated impurities for safe disposal)